Globalized economy
The world - Globalization
978-3-14-100790-9 | Page 194 | Ill. 1
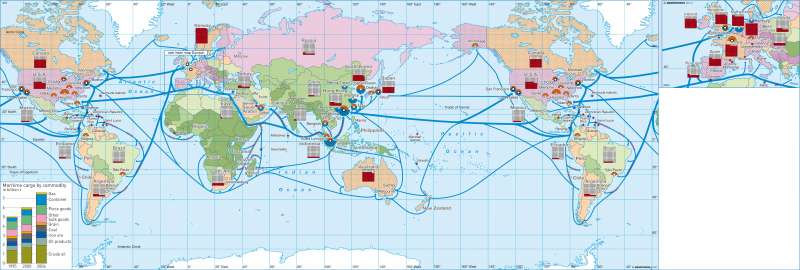
Information
In the last three decades the world economy has seen a strong increase in international linkages. This was significantly greater that the growth of world economic productivity in the same period, as measured in the GDP of the nations of the world. This process of emergence of global systems of production and consumption is customarily referred to as globalization.Development of World Exports and World Economic Productivity
The decisive prerequisites for the expansion of international relationships were, on the one hand political decisions to reduce existing barriers to economic relations between countries, and on the other hand the development of the material infrastructure. The political measures were driven by the idea that international exchange would permit the optimal use of resources and factors of production, save costs, and contribute to the economic development of all the participating nations. Key political decisions setting the course in this direction included the accords of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which led to the establishment of the WTO (World Trade Organization); this world trade order promoted liberalization, for example by reducing customs duties and abolishing non-tariff trade barriers, and a level playing field for all participants — at least in formal terms — thus making the international exchange of goods significantly easier. The agreements of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) led to the emergence of a world currency regime in which foreign exchange restrictions were dispensed with and free convertibility of