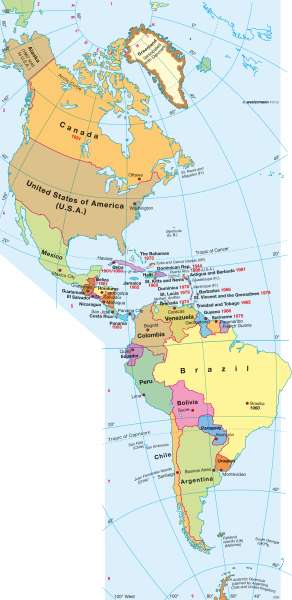
America — Political map
The Americas - States and history
978-3-14-100790-9 | Page 125 | Ill. 4
Information
After a chequered history, Canada moved towards autonomy and regional concentration through the Statute of Westminster from 1931, in which it became independent. Newfoundland joined in 1949 as the tenth province. In the former French and still largely French-speaking province of Quebec, separatist aspirations repeatedly came again in the second half of the 20th Century.In 1849, the territory of Oregon (in the western United States) consisted of present-day states of Oregon, Washington, Idaho and parts of Montana. Oregon was admitted into the Union in 1859, followed by Washington and Montana in 1889 and Idaho (1890). The last states to join the Union and which gave United States its present form, were Oklahoma (1907), Arizona and New Mexico (both 1912), Hawaii and Alaska which in 1867 was bought from the Russians (both 1959).
Greenland, which was Danish-owned since the start of the 18th Century and recognised since 1953 as an equal part of the Kingdom, had a new autonomy statute after a referendum in 1979. Since then, Denmark set the foreign, defence and monetary policies of the island, while the economic, social and cultural policies are the tasks of the Greenland government. About 85% of over 50,000 inhabitants are Inuit.
Nations in Central and South America
In Central America, there are essentially still the boundaries that were created in the process of nation building in the early 19th Century. More recent examples are the states of Panama, which in 1903 became independent from Colombia, and Belize (formerly British Honduras)-was given limited autonomy in 1964 and since 1981, has been independent. Although there is a government, Queen Elizabeth II remains head of state. Belize is represented by a governor. The Caribbean islands have acquired their independence, mainly in the second half of the 20th Century.
In South America, the boundaries have shifted somewhat since 1825, without changing significantly the nation's outline. Guyana is now divided into the countries of Guyana (1966, formerly British), Suriname (1975, firstly Dutch) and the former penal colony of French Guiana. The Chaco War in the 1930's, between Bolivia and Paraguay changed the borders. Some parts of southern Peru had to give up land to Chile, before expanding in 1942 to the north at the expense of Ecuador. The Falkland Islands in the far south came under Argentinian occupation in 1982, which triggered a war with Britain. The war ended in a victory for the British troops.
K. Lückemeier; Ü: Colette Fleming