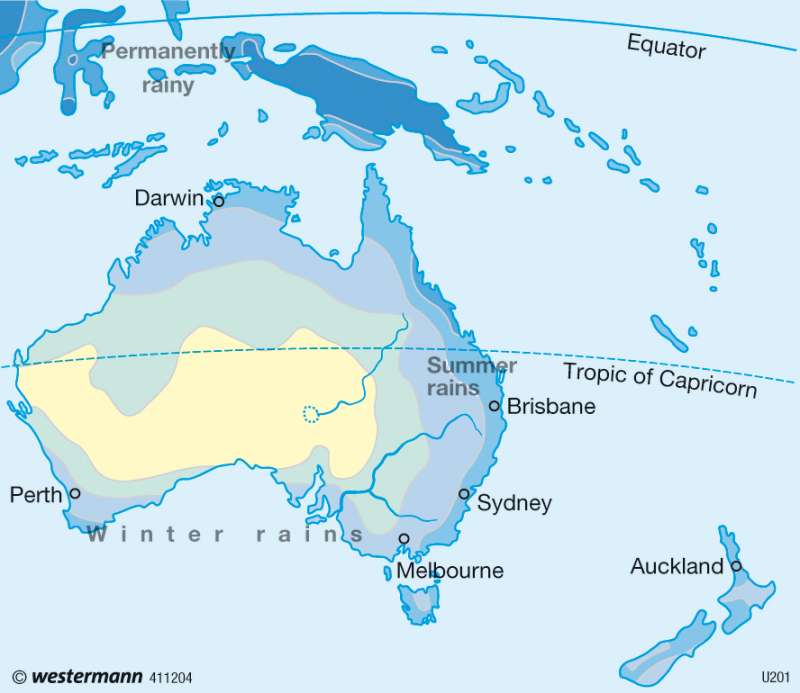
Annual precipitation
Australia and New Zealand
978-3-14-100790-9 | Page 120 | Ill. 2
Information
Large parts of Australia are solar-climatic in the area known as the tropics and subtropics. The boundary between them passes near the southern tropic. Here, the dominant influence of the high-pressure belt of the southern hemisphere characterises the climate of large parts of the continent. The combination of windward-leeward effects and high altitude creates such a wide range of climatic conditions between dry and frequently humid tropics and between dry and moist subtropic summer and winter. In the area of Tasmania, Australia extends to the south right up into the southern mid latitude, as does New Zealand. With a few exceptions, the Pacific islands lie in the tropics.Annual precipitation
While Indonesia has, in part, annual precipitation of over 3,000 mm in a long-term average, rainfall in
Australia is largely much lower. The highest values found are along the eastern, northern and southern reaches of the continent. On average, 500 to 1,000 millimetres fall. Even the barrier of the Australian highlands has over 2,000 millimetres of annual precipitation. However, in interior and western Australia, values sometimes reach less than 250 millimetres and therefore are characterised by a pronounced drought.
New Zealand and the Pacific Islands are familiarised with dominant wind directions (Passat or westerlies) windward-leeward effects are particularly noticeable in mountains that aren"t noticeable on the map because of the significant scale.
A. Siegmund; Ü: Colette Fleming