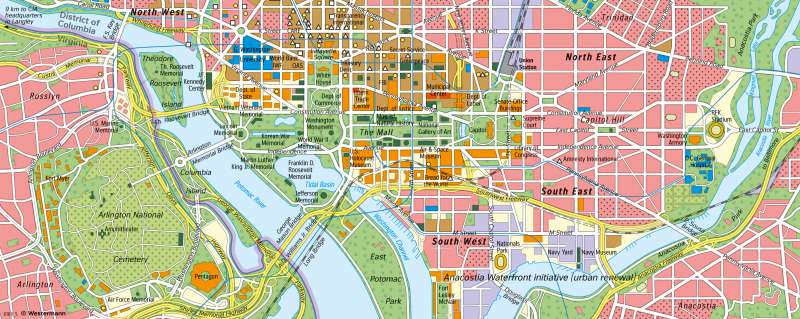
Washington, D. C. - The centre of U.S. political power
East Coast cities
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 191 | Ill. 5
Overview
The political centre of the USA is the federal capital Washington D.C., the seat of the president, the federal government, Congress and important international organisations, among others. The cityscape is characterised above all by its numerous representative buildings, most of them built in a historicist style. Washington D.C. has 706,000 inhabitants. The African American population dominated for decades, but in 2011 its share fell below 50 percent again for the first time. A large part of the population lives on incomes below the poverty line. Only the Georgetown district, which is dominated by a white population, is considered prosperous. The university of the same name is located on its western edge.
Outline of a capital city
The centre of Washington was laid out on the north side of the Potomac according to a design by the Frenchman L'Enfant and initiated by George Washington in 1790. Similar to Manhattan (see map 190.3), the strict chessboard pattern stands out, but more strongly interrupted by diagonals. The naming of the streets - as far as not numbered - has been determined by American history. In addition to states such as New York, Massachusetts, Virginia and Pennsylvania, there are key words such as Independence and Constitution. The diagonals are each aligned with squares at their intersections.
At two of these intersections stand the Capitol and the White House, the central buildings of the capital, both with a high symbolic value. The White House was built in the classicist style from 1792 onwards and is the residence and official residence of the American president. The Capitol, with its distinctive dome structure, is the parliamentary seat where the Senate and the House of Representatives meet. Its construction began in 1793 but it was not completed until the mid-19th century. The name was taken from one of the seven hills on which Rome was built. In the immediate vicinity of the Capitol are other important parliamentary buildings: House Office Building, Senate Office, Supreme Court, and the Library of Congress. At the intersection of the two axes radiating from these buildings stands the Washington Monument, which commemorates the city's founder, namesake, and first president of the USA. The Lincoln Memorial near the Potomac and the Roosevelt Memorial on the island of the same name in the Potomac also commemorate outstanding American presidents. Between the Washington Monument and the Capitol are the parks known as "The Mall", which are lined with numerous federal agencies - including the Departments of Justice, Agriculture and Commerce, the FBI and NASA - and cultural institutions. The departments correspond to the federal ministries in Germany.
Just outside the city limits in Arlington (Virginia) is the Pentagon, the pentagonal building of the Department of Defense erected in 1941/42, surrounded by numerous other military facilities and monuments (for example, the National Cemetery). Military facilities, for example those of the Navy, are also located in southern Washington. In addition to government agencies, Washington is home to numerous educational institutions.
Institutions of the United Nations
The World Bank, officially known as the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, is a United Nations agency. The World Bank grants loans to finance specific projects and - in the case of crises - for structural adjustment, mainly to developing countries and the transition states of Eastern Europe. Its policy is not without controversy, because the granting of loans is linked to conditions through which it exerts influence on the projects and the respective governments. Since its directors are seconded by the World Bank's five largest donors and its president is always a US-American, the World Bank is clearly dominated by Western interests.
Like the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund is a UN organisation. Its task is to monitor the international monetary system - above all the exchange rate and monetary policies of the member states - and to safeguard against international financial crises that can be triggered by strong fluctuations in exchange rates. The USA and the EU countries together each have a veto right over decisions.
Moreover, many international non-governmental organisations (NGOs), such as Amnesty International, have their headquarters in Washington.
Institutions of the United Nations
The World Bank, officially known as the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, is a United Nations agency. The World Bank grants loans to finance specific projects and - in the case of crises - for structural adjustment, mainly to developing countries and the transition states of Eastern Europe. Its policy is not without controversy, because the granting of loans is linked to conditions through which it exerts influence on the projects and the respective governments. Since its directors are seconded by the World Bank's five largest donors and its president is always a US-American, the World Bank is clearly dominated by Western interests.
Like the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund is a UN organisation. Its task is to monitor the international monetary system - above all the exchange rate and monetary policies of the member states - and to safeguard against international financial crises that can be triggered by strong fluctuations in exchange rates. The USA and the EU countries together each have a veto right over decisions.
Moreover, many international non-governmental organisations (NGOs), such as Amnesty International, have their headquarters in Washington.