Universe - Our galaxy, the Milky Way
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 10 | Ill. 1
Overview
All the stars shown on the star chart belong to the Milky Way and are more or less in the cosmic area surrounding the Sun. The bright and medium-bright stars are distributed fairly evenly across the sky. However, the fainter the stars become, the more they concentrate towards the narrow part of the Milky Way in the sky. This suggests that the majority of faint - and therefore generally distant - stars form an oblate system.
Spiral galaxies
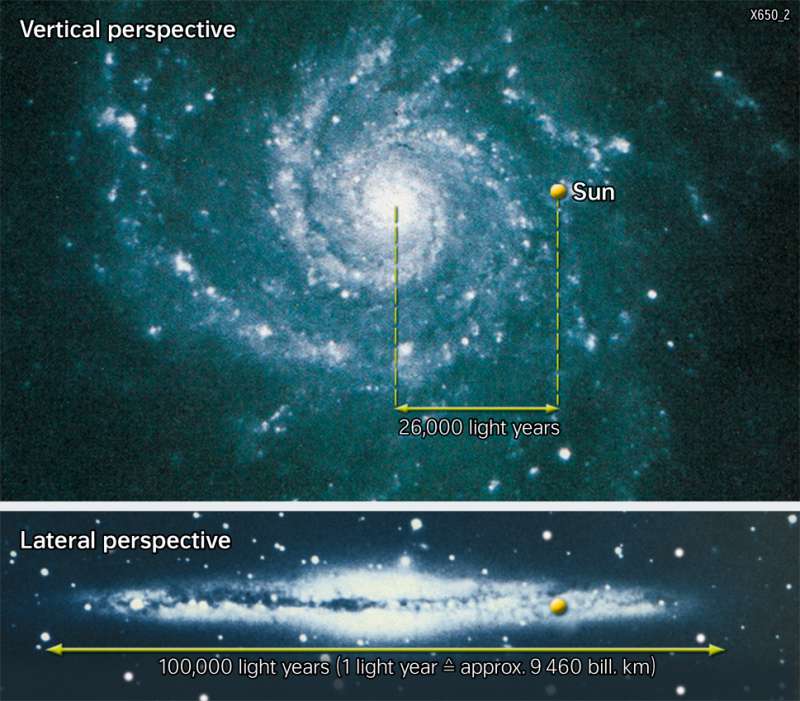
In fact, viewed from the outside, the Milky Way has a disc-shaped structure with a bulging core and spiral arms. Spherically arranged around it are the cosmically very old "globular clusters", which look spherical and consist of up to several hundred thousand stars (indicated as spheres in the lateral perspective). The entire system consists of a total of more than 100 billion stars, which account for about 85 to 90 per cent of the total mass, as well as clouds of interstellar gas with some dust mixed in, from which stars are formed and to which they release the part of their matter that does not remain in "stellar corpses" at the end of their life. The dust in such clouds can be recognised as dark stripes in the side view of the Milky Way and as dark sub-areas of the Milky Way in the star chart, because the dust obscures the light of the stars behind it. The Milky Way also rotates on its axis. The Sun is about 26,000 light years away from its centre and takes approximately 250 million years to orbit.
Galaxy clusters and superclusters
Most of the galaxies are found in such galaxy clusters, most of which consist of much more members (up to thousands of galaxies) than the Local Group (about 40 members). Galaxy clusters are not yet the largest hierarchical structure in the universe. These are called superclusters. We belong to the Virgo supercluster. Only recently it was discovered that superclusters have a string-like structure.
However, this only counts for the matter in the universe which can be observed because it is radiating in some range of the electromagnetic spectrum, for example in the visible light or in the X ray range. Today we know that this adds up to only 15% of the matter in the universe. The rest is “Dark Matter†which can be noticed only by its gravitational action.
Distances in space
. All visible stars belong to the Milky Way, our Galaxy. The centre of the Milky Way is about 26,000 Ly away from the Sun while the entire Milky Way has a diametre of about 100,000 Ly. The Andromeda galaxy (which still can be observed with the naked eye) has a distance of about 2 Mio. Ly. Like the Milky Way, it belongs to the “Local Group†- this is the name of our galaxy cluster.