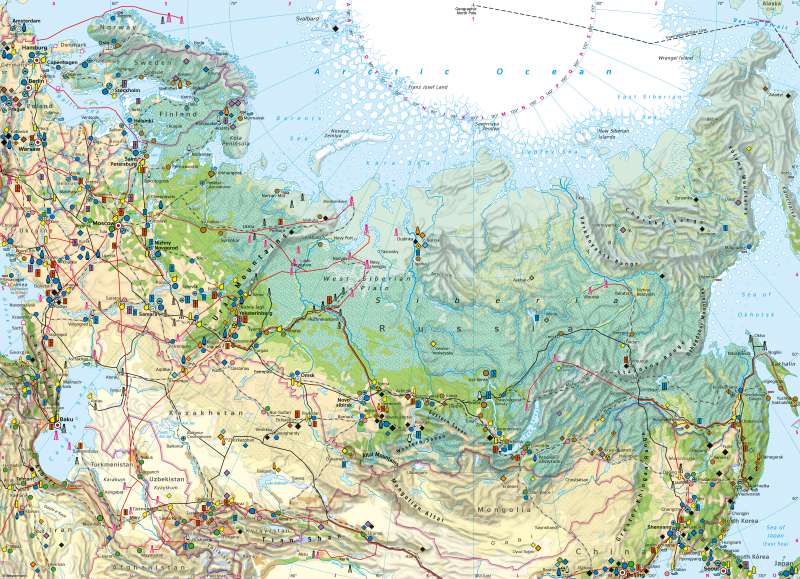
Russia and Central Asia - Economy and land use
Economy and land use
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 112 | Ill. 1
Overview
Hardly any other country has as many natural resources as Russia. The range of mineral resources is diverse. In addition, more than one-fifth of the world's forests and around one-fourth of the available fresh water can be found there.
Russia is a major producer of energy raw materials. It produces the world's second-largest amount of natural gas by country (after the USA) and the third-largest amount of oil (after Saudi Arabia and the USA), and also has the second-largest coal reserves. However, the close linkage of its economy to oil and gas exports also makes Russia's economy vulnerable - due to fluctuating world market prices. The main market for Russian energy raw materials is Europe.
Looking at some economic regions
The Urals, southern Siberia and the Kursk region are the focal points of ore processing. Metal processing plants have been built near the centres of the smelting industry. Mechanical engineering and vehicle construction are concentrated around Moscow, Saint Petersburg and in the cities along the Volga, chemical plants and oil refineries in Siberia along the Trans-Siberian Railway. Other industrial centres are the areas between the Urals and Moscow, Samara on the Volga and Saint Petersburg. Wood processing is focused in two areas: One chain of mills stretches from Arkhangelsk through Narjan-Mar to Salechard on the Ob River, and another runs along the Trans-Siberian Railway from the Urals to Irkutsk. The undisputed business, trade and financial centre is the metropolitan area of Moscow, which has a good 15 million inhabitants and holds a key position for the Russian economy.
The former Soviet republics have developed in different ways. The Baltic states of Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia have been members of the EU since 2004 and - despite some deficits - are increasingly integrated into European economic structures. Belarus, which is isolated in foreign policy terms, suffers from an economy in great need of modernisation.
Ukraine's economy has been weakened by domestic political strife and the fighting in the east of the country. The country is traditionally an agricultural area. Other economic sectors include the metallurgical and chemical industries, mechanical engineering, and the food industry. An important mining and industrial area is the Donetsk Basin.
Some Central Asian states such as Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan benefit, like Russia, from the wealth of energy raw materials. They have established sites for the oil-processing industry and developed into important exporters. In the countries of Central Asia, the cultivation of cotton and its further processing (textile industry) has a long tradition, but due to the necessary artificial irrigation, the region also has dramatic environmental problems (for example, the Aral Sea). Mongolia's economic growth is based on its significant deposits of copper, coal, zinc, uranium, oil, rare earths and gold.