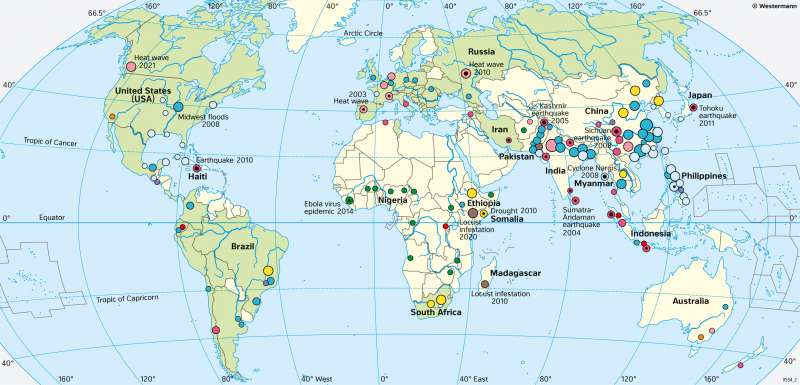
The World - Natural disasters in the 21st century
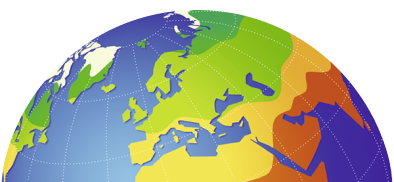
Ecozones and natural hazards
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 23 | Ill. 4
Overview
In the first decades of the 21st century, millions of people died as a result of natural disasters. The high number of victims results, on the one hand, from the global increase in population, and, on the other hand, from the greater concentration of population in regions at risk, especially along coasts.
Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
On 26 December 2004, the Sumatra-Andaman earthquake occurred in the Indian Ocean, the third strongest earthquake in recorded history. The Earthquake and subsequent tsunamis killed 230,000 people and left 1.7 million homeless. Most of the deaths occurred in Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
The Kashmir earthquake in October 2005 killed over 85,000 people, mostly in Pakistan, and an earthquake in Sichuan, China, in May 2007 killed nearly 70,000 people and destroyed millions of buildings. The most devastating earthquake in recent years occurred in Haiti in January 2010. With an official death toll of 316,000, it was the worst earthquake in the history of North and South America. The Tohoku earthquake off the east coast of Japan on 11 March 2011 was the most expensive in history so far, with damages of around 335 billion US dollars. The Earthquake and tsunami killed 19,300 people and triggered a nuclear disaster at the Fukushima nuclear power plant. Hundreds of thousands of people fled or had to be evacuated and infrastructure was destroyed over a wide area.
Thanks to improved forecasts, there were significantly fewer victims of volcanic eruptions. The largest number of victims was caused by the eruption of Mount Merapi on Java (Indonesia) in 2010, which claimed more than 300 lives.
Devastating storms
Devastating hurricanes occur every year. In 2003 and 2004, Hurricanes Isabel and Ivan killed nearly 150 people in the Caribbean and southeastern USA. In the 2005 hurricane season, four hurricanes of the highest category were recorded in the Atlantic alone, including Hurricane Katrina, which is considered one of the worst natural disasters in US history, with over 1,800 deaths and US$ 108 billion in damages.
One of the worst cyclones ever in the South Asian region was Cyclone Nargis, which killed nearly 140,000 people in Sri Lanka, India, Bangladesh and Myanmar in April and May 2008. Typhoon Haiyan killed over 6,000 people in the Philippines, China and Vietnam in November 2013.
Epidemics
Ebola fever, which spread to several West African countries from 2014 onwards, sickened almost 30,000 people and killed more than 11,000. The epidemic has been considered over since the beginning of 2016.
In autumn 2019, a new animal-to-human transmitted infection from the group of Corona viruses (Covid-19) occurred in China (presumably in the megacity of Wuhan). Since then, the disease has spread rapidly and in several waves across the entire globe. It mainly affects older and pre-diseased people. In March 2020, almost 125 million people were already evidently infected, 2.7 million of whom died. In August 2021, the number of cases increased to over 200 million while 4.3 million deaths occurred.
So-called "lockdowns", a partial or almost complete shutdown of economic and social life for the purpose of combating the virus, have generated considerable economic and social costs in many countries, the medium and long-term consequences of which are not yet foreseeable. Additionally, vaccines were created to stop the virus from spreading.
Drought and heat
Parts of East Asia and Africa were particularly hard hit by droughts. In Somalia, the major drought of 2010/2011 coincided with a civil war - with disastrous consequences: According to FAO, more than 250,000 Somalis died of malnutrition between October 2010 and April 2012 and deaths in famine also occurred in Ethiopia and Kenya.
In Europe, a prolonged heat wave with temperatures above 40°C in August 2003 led directly or indirectly to the death of an estimated 70,000 people. Spain and Portugal were particularly affected, but also northern Italy, France, and other countries. Consequence of the record heatwave in Eastern Europe in 2010 were severe crop losses and devastating forest fires around Moscow.
River floods
Asia is hit worst by floods. Bangladesh was hit by one of the worst flood disasters ever in 1991, when a cyclone inundated large parts of the country and killed nearly 140,000 people. In 2007, almost one million people were affected by floods in southwestern Pakistan, and in August 2008, flooding occurred in the Indian state of Bihar after weeks of monsoon rains. In July and August 2010, Pakistan was again hit by floods after heavy monsoon rains. Almost 2000 people died, and millions were dependent on humanitarian aid.
Flood disasters on a much smaller scale occurred in Europe when the Danube burst its banks in many places in Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria in 2006, washing away entire villages. Two other floods in 2010 and 2013 caused deaths and severe devastation in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Poland, the Czech Republic, and countries bordering the Danube.