The World - Economic output
Economy
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 46 | Ill. 2
Overview
Gross National Income (GNI) is a widely used standard indicator to compare the economic performance of countries. The gross national income of a year indicates the value of all goods and services produced in that year by companies, authorities, and individuals of a country, both at home and abroad. Thus, for GNI, the place of production is irrelevant.
Another indicator of economic performance, the gross domestic product (GDP) of a period, indicates the value of all goods and services produced during that period by an economy within the national borders of the respective state. It does not matter whether this was done by domestic or foreign companies, authorities, or persons. For GDP - unlike for GNI - the place of production is decisive.
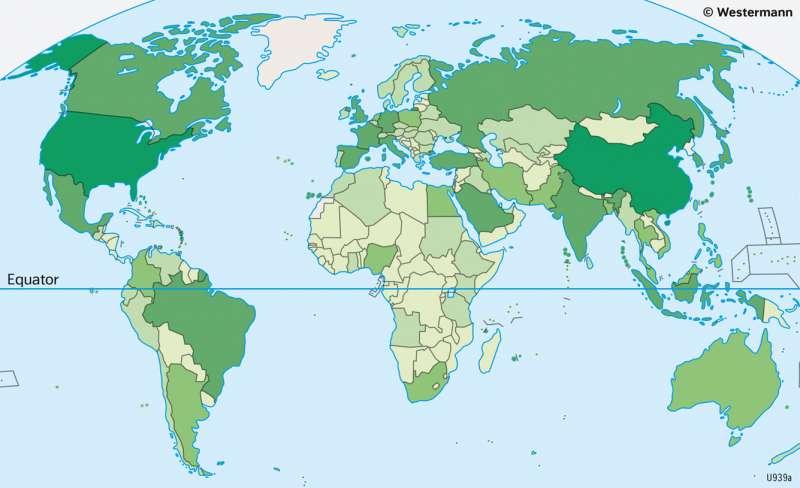
GNI in absolute values
This map shows gross national income by country in absolute values. As it presents, gross national income varies greatly in international comparison. The highest absolute values are achieved primarily by highly developed countries with large populations and emerging economies, but also by less developed countries such as Nigeria, for example, if they have significant raw material production (oil) or are strongly integrated into global trade flows as low-wage production locations for various industries. The regions of the triad clearly stand out as economic centres (North America, Europe, parts of East and Southeast Asia). The absolute statements on gross national income enable meaningful comparisons: Germany alone, for example, has an economic output equivalent to that of the entire continent of Africa.