The Earth - Solar radiation
Atmosphere and climate change
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 20 | Ill. 2
Overview
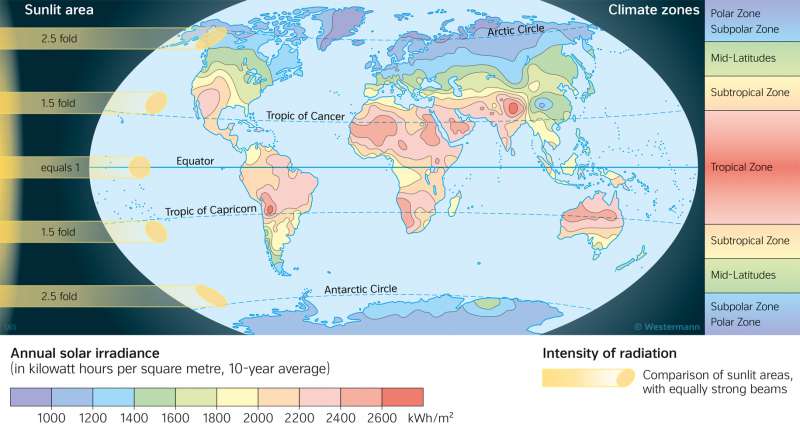
Global radiation is the total radiation from the Sun that reaches a certain horizontal section of the Earth's land surface in the course of a year. It includes both direct radiation and diffuse radiation deflected off particles in the atmosphere.
Solar radiation and thermal climate zones
Due to the curvature of the Earth's surface and the position of the Earth in relation to the Sun, a beam of radiation of the same intensity does not strike an equally large area everywhere. The area is 2.5 times larger near the poles than at the equator (see the yellow areas on the map). Therefore, the radiation intensity decreases from the equator to the poles. Thus, the global radiation results in the four major thermal climate zones: Polar Zone, Mid-Latitudes, Subtropical Zone and Tropical Zone.
Across the Earth, the lines of equal global radiation and thus the thermal climate zones have a zonal arrangement. However, this is only ideal for the Cold Zone and the Mid-Latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere.
Particularly above the large continents, the lines of equal global radiation or the thermal climate zones often do not run parallel to the latitude circle. For example, above Tibet an area of highest global radiation can be seen far to the north at a relatively large distance from the equator. In the southern part of Africa, areas of very high global radiation are located much further south than in South America, for example, and in North and Central America much further north than in Europe. The reason for this is the formation of high-pressure areas over extensive land masses that heat up strongly in summer. Low cloud cover ensures high levels of direct solar radiation there.
In contrast, areas with warm, relatively humid ocean currents have a high cloud formation. This reduces direct solar radiation and leads to comparatively low values of global radiation, for example in the coastal areas of the North Atlantic or in East Asia.