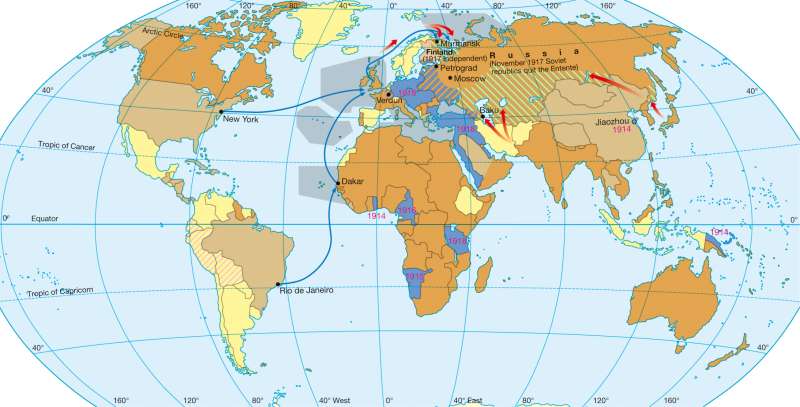
The world during World War One (1914 — 1918)
The world - The age of imperialism
978-3-14-100790-9 | Page 185 | Ill. 3
Information
Alliances on the Eve of WarIn 1882, a secret military alliance (Triple Alliance) between Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy had concluded. Italy signed a secret treaty around 1902 with France, while in1914, first declared its neutrality when it entered the Entente Cordiale 1915. The Triple Alliance were the Central Powers which joined the Ottoman Empire in 1914, and then Bulgaria in 1915. The Triple Alliance was the starting point for further European treaties of alliance from the turn of 19th to 20th Century, not least because of the implicit orientation towards Russia and France.
Since 1892, an alliance relationship had existed between France and Russia, between France and Great Britain since 1904 (the Entente Cordiale) and between Britain and Russia since 1907 (St. Petersburg Treaty). These three states formed the core of the Triple Entente. Between Britain and Japan, as well as Russia and Japan, it was kept secret that in 1914 Japan made allies in Asia. Important allies which joined the war were Italy (from 1915) and the United States (from 1917) with the mother countries and the colonies included in the pacts.
Results of the War
The collapse in Europe after the defeat of the Central Powers of the Austria-Hungary deal meant Germany was forced to surrender large territories and its colonies. In south-eastern and central Europe, this led to numerous new and re-established nation states. Perhaps the most important world political result was the formation of Soviet Russia following the Octobe