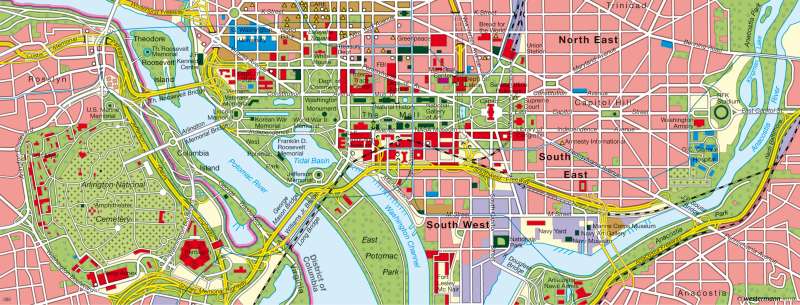
Washington D.C. — The U.S. centre of power
U.S.A. - Cities in the North-East
978-3-14-100790-9 | Page 143 | Ill. 5
Information
Washington is part of a large volume of compressed settlements in the northeastern U.S., ranging from Boston to north of New York, Philadelphia and Baltimore, to Washington in the south and commonly known as "BosWash" (short for "from Boston to Washington"). The city lies on the Potomac, at a point where the river is greatly enlarged and virtually becomes an extension of the deeply branched Chesapeake Bay. Unlike its neighbouring cities, Washington has no industrial centre, but the west is almost exclusively determined by its function as the capital city with the White House and administrative seat of the World Bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF).Layout of a capital
After the 1790 draft initiated by George Washington, the centre of Washington was created on the north side of the Potomac by Frenchman Pierre L'Enfant. The strict chequerboard pattern is strikingly similar to Manhattan (see map 208.1), but is more broken up by diagonals. The naming of streets, if not consecutively numbered, has been strongly influenced by American history. In addition to states like New York, Massachusetts, Virginia and Pennsylvania, there are key words such as "Independence" and "Constitution". The diagonals are aligned in their respective positions at intersections.
On two of these crossing points are Capitol Hill and the White House, the central building of the capital, both of which have high symbolic value. The White House was built around 1792 in a classical style and is the residence and office of the American President. The Capitol building, with its distinctive dome, is the seat of parliament, where the Senate and the House of Representatives meet. It was started in 1793, but was not completed until the mid-19th Century. The name was taken from one of the seven hills on which Rome was built. In the immediate vicinity of Capitol Hill are other important institutions of Parliament: House office buildings, the Senate Office, Supreme Court and the Library of Congress.
At the intersection of the two axes emanating from these buildings, is the Washington Monument which commemorates the city's founder, its namesake and first president of the United States. Also, the Lincoln Memorial near the Potomac and the Roosevelt Memorial, on the island in the Potomac, which commemorate prominent American presidents.
Between the Washington Monument and Capitol Hill are the parks of "the Mall", lined with numerous federal agencies including the Department of Justice, Agriculture and Commerce, the FBI and NASA and other cultural institutions. The departments are all Ministries of the United States.
The Pentagon is located outside the city limits of Arlington (Virginia), the Department of Defense five cornered building (built around 1941/42), is among many military facilities and monuments such as the National Cemetery. Other military facilities, such as the Navy, are found to the south of Washington. In addition to government agencies, numerous educational institutions are also located in Washington.
M. Felsch; Ü: C. Fleming