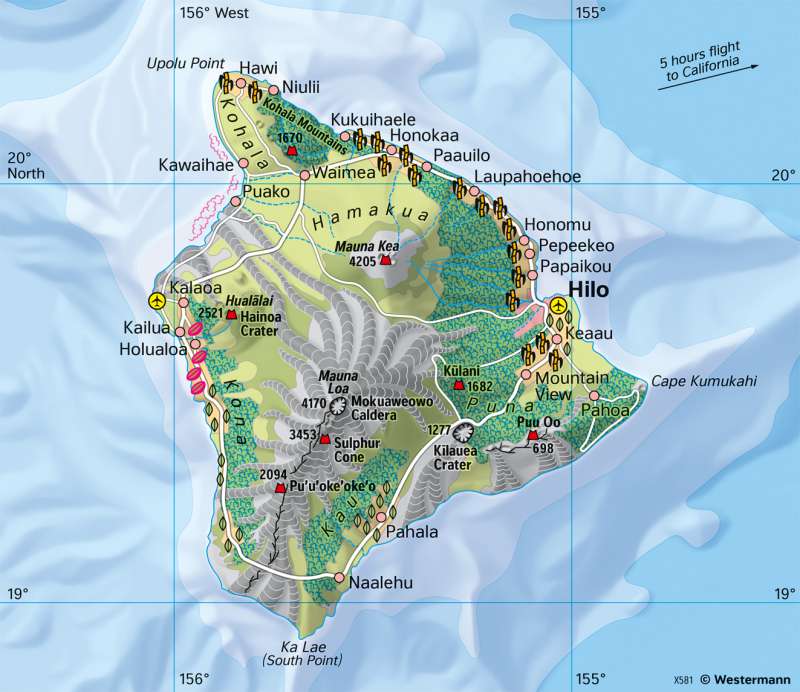
Hawaii - Volcanic island
Topographic orientation
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 161 | Ill. 2
Overview
The Hawaiian Islands are a group of islands in the central northern Pacific Ocean. Their mainland area is just under 17,000 square kilometres. In addition to the four large main islands of Hawaii, Maui, Oahu (with the capital Honolulu) and Kauai, the archipelago includes over 120 smaller islands, many of which are uninhabited. Hawaii has more than one million inhabitants and is a state of the USA.
Volcanic islands
The Hawaiian Islands owe their formation to the intersection of two tectonic lines (with northwest and northeast strike directions). The islands are built up by huge volcanic cones, and coral reefs and limestones also play a role, especially in the smaller islands. The lava that pours from the vents of the large active volcanoes is thin and forms lava flows on the slopes. It builds shield volcanoes with slopes of up to 10 degrees. Sudden eruptions with catastrophic effects (as for example at Vesuvius) do not occur in Hawaii because of the calm lava flow.
The Hawaiian Islands are a typical example of the formation of an island chain by hotspot volcanism (see image in the atlas). In this case, there is a melting area in the Earth's mantle from which magma rises in vents to the Earth's surface. The melting area itself does not change its location. If the Earth's plates move relatively evenly in a constant direction above it, new volcanoes are formed again and again. These extinguish with increasing distance from the melting area. This creates a chain of volcanoes of varying activity and age, arranged like a string of pearls.
The island of Hawaii, which gives its name to the archipelago, is the largest of the islands with a land area of 10 400 square kilometres. Hawaii's most famous volcanoes are Mauna Kea (not actie), Mauna Loa (active) and Kilauea (active) on the western flank of Mauna Loa.
If you measure the height from the bottom of the sea to the sea surface, Mauna Kea, at more than 10,000 metres, is still significantly higher than Mount Everest (8848 m). To get from the coast to the summit of Mauna Kea, it only takes about two hours by car. The highest astronomical observatory on earth is located on the summit of Mauna Kea, and another volcanic observatory is located on Kilaulea.
History
The Hawaiian Islands were settled by Polynesians from 800 AD. Europeans first discovered Hawaii in 1778, represented by James Cook, who was looking for a northern passage from the Pacific to the Atlantic ("3rd voyage"). He gave the archipelago the name Sandwich Islands. Around 1800, the islands were united as a kingdom, but fell under American influence in the second half of the 19th century. In 1898 they were annexed by the United States, by then declared a republic, and since 1959 they have been the 50th state of the USA.
Today, the Hawaiian Islands are an important tourist area, a US military base, and agricultural cultivation area for sugar cane, coffee, and fruit (pineapples, bananas), among other things. Cultivation on the drier leeward side partly requires additional irrigation.
Climate contrasts
Due to its location in the tropics, temperatures in Hawaii are warm and balanced throughout the year. However, apart from the altitude gradation, a contrast is noticeable between the northeast and southwest exposed coasts. In the northeast, there are most settlements, intensively used cultivation zones and a more or less wide strip of rainforest, a relic of the original vegetation. These forests are missing in the east and south of the island. The reason for the contrast is the spatial distribution of precipitation on the favoured windward sides and the disadvantaged leeward sides.
In summer, northwest-southeast trade winds predominate. These blow with extraordinary constancy. As a result of upslope processes on the high mountains of the islands, precipitation is among the most intense on earth (at Mount Waiale on the neighbouring island of Kauai, the average annual precipitation is 12 547 mm). However, the highest precipitation does not fall on or at the mountain peaks, but at medium altitudes (around 1500 metres).
On the map, the contrast between the windward and leeward sides is also evident from the fact that there are no rivers in the east and south and the few rivers in the northeast only carry water intermittently, while the rivers on the windward side are numerous and mostly carry water constantly. Equally striking is the difference between the north and south slopes of the range where Kilauea is located.
History
The Hawaiian Islands were settled by Polynesians from 800 AD. Europeans first discovered Hawaii in 1778, represented by James Cook, who was looking for a northern passage from the Pacific to the Atlantic ("3rd voyage"). He gave the archipelago the name Sandwich Islands. Around 1800, the islands were united as a kingdom, but fell under American influence in the second half of the 19th century. In 1898 they were annexed by the United States, by then declared a republic, and since 1959 they have been the 50th state of the USA.
Today, the Hawaiian Islands are an important tourist area, a US military base, and agricultural cultivation area for sugar cane, coffee, and fruit (pineapples, bananas), among other things. Cultivation on the drier leeward side partly requires additional irrigation.